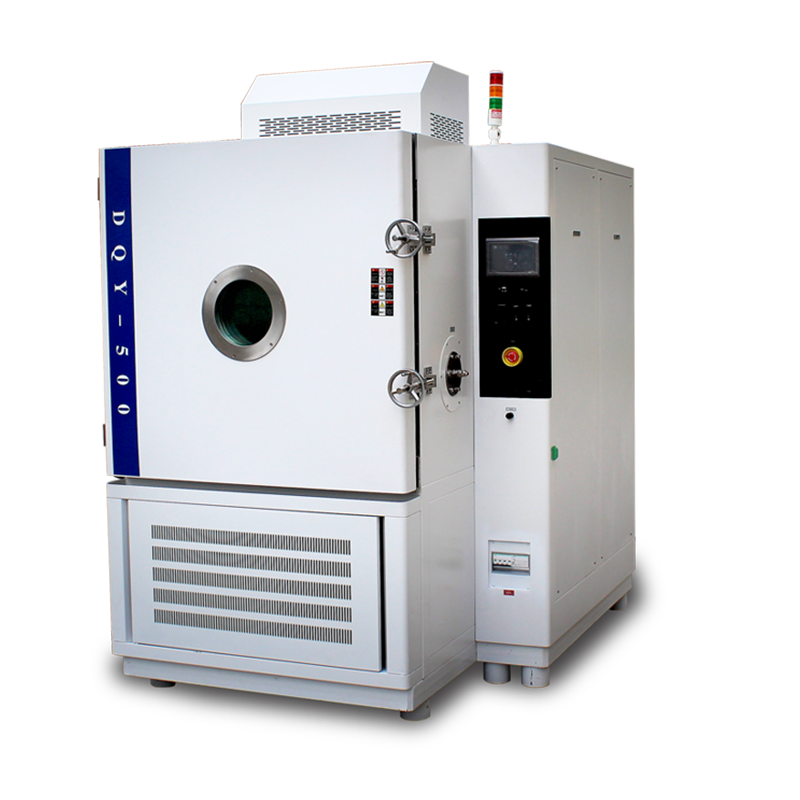
A low-pressure test chamber is equipment used to simulate high-altitude environments, widely applied in product testing for industries such as aviation, aerospace, and electronics. Safe operation of these chambers is critical not only for ensuring test accuracy but also for protecting operator safety and preserving the equipment. The following details the safety protocols for operating low-pressure test chambers, aimed at helping relevant companies and research institutions strengthen their safety management.
1. Operator Qualifications
- Specialized Training: Operators must undergo specific training to understand the principles of low-pressure testing, the chamber's structure, and operational procedures. They must be proficient in identifying all equipment functions and safety features.
- Safety Awareness: Operators must possess strong safety awareness, understand the potential risks associated with low-pressure environments, and be capable of implementing appropriate protective measures.
2. Equipment Inspection and Maintenance
-
-
- Regular Checks: Before each tesquipment.
- Fault Handling: If any equipment malfunction is detected, usage must cease immediately. Notify qualified maintenance personnel for repair. Under no circumstances should operators attempt to disassemble or modify the equipment themselves.

-
3. Standard Operating Procedures
- Environmental Preparation: Ensure the laboratory environment meets the requirements for low-pressure testing. Parameters such as temperature and humidity should be within recommended ranges to avoid compromising test results.
- Pre-Test Confirmation: Before initiating a test, operators must confirm that the test plan is understood, the sample is securely fastened, and all safety measures are in place to prevent accidents during pressure changes.
4. Safety Measures During Testing
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Operators must wear appropriate PPE, such as safety glasses and gloves, before conducting low-pressure tests to prevent injury in case of an incident.
- Ventilation: Maintain adequate ventilation facilities within the low-pressure test environment to prevent the hazardous accumulation of gases.
5. Emergency Response Plan
- Emergency Exits: Ensure all emergency evacuation routes in the laboratory are clear and unobstructed. Conduct regular drills so all personnel are familiar with escape routes during an emergency.
- Emergency Shutdown: If any abnormality occurs during a test, immediately press the emergency stop button to halt the experiment and ensure the safety of both personnel and equipment.
6. Post-Test Procedures
- Documentation: Upon test completion, promptly record and save all relevant data for subsequent analysis and traceability.
- Site Cleanup: Restore the laboratory to its original state. Clean up any waste generated during testing to maintain a tidy and safe laboratory environment.
As high-precision equipment, strict adherence to the safety operating procedures for low-pressure test chambers is paramount. Following the protocols outlined above effectively minimizes risks and ensures experiments proceed smoothly. Companies and research institutions should integrate these standardized procedures with a strong safety culture to build a solid foundation for technological innovation and development. Safe operation remains the foremost priority for achieving efficient testing and guaranteeing life safety.