In modern industrial manufacturing, electronic device R&D, and automotive component testing, product reliability is paramount. Products must maintain stable performance in extreme environments—whether in intense cold or high heat—to prevent safety hazards or negative user experiences. Thermal shock chambers (also known as temperature and humidity cycling test chambers) are essential tools for simulating these harsh conditions, helping companies identify potential issues before products reach the market and thereby improving quality.
But how can we ensure the accuracy and reliability of test results? This requires adherence to strict testing standards. This article will provide an in-depth analysis of the main test standards for thermal shock chambers and explore their applications across various industries to help you select the most suitable testing solution.
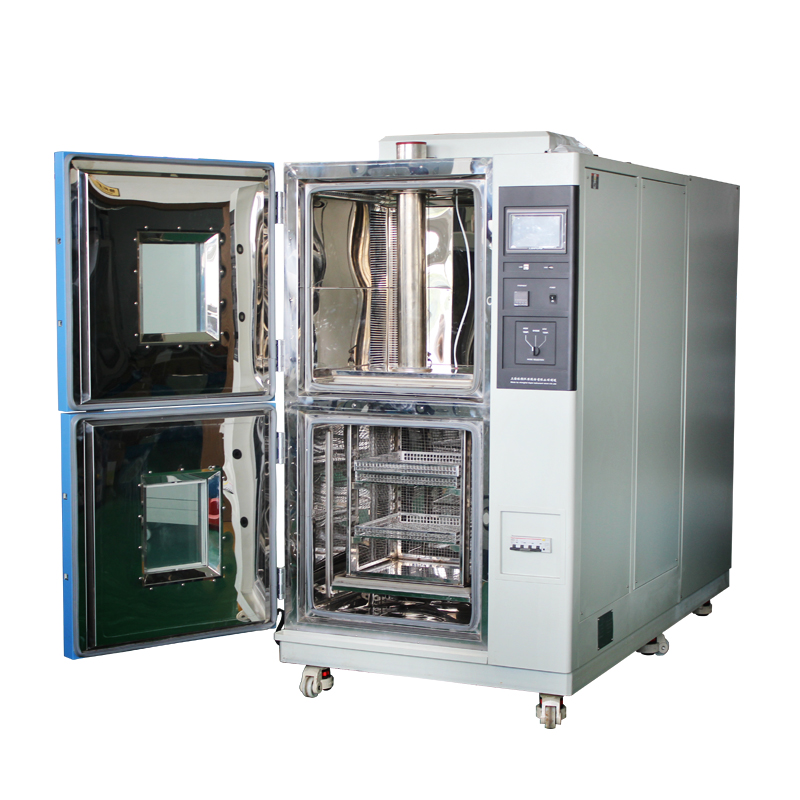
1. Basic Principles of Thermal Shock Chambers
A thermal shock chamber is equipment capable of simulating environments with extreme temperature variations. It tests a product's ability to withstand conditions like thermal shock, temperature cycling, and damp heat aging by precisely controlling the internal temperature (e.g., -70°C to +150°C) and humidity (e.g., 20% RH to 98% RH).
Key features include:
- Rapid temperature ramping (e.g., 15°C per minute)
- Precise temperature and humidity control (e.g., ±0.5°C)
- Programmable cyclic tests (simulating day/night or seasonal changes)
However, having high-performance equipment alone is not enough. The choice of testing standards directly impacts the scientific validity and effectiveness of the tests.

2. Key Test Standards for Thermal Shock Chambers
Different industries and applications have varying testing requirements, leading to the establishment of international standards to ensure consistency and comparability. The most commonly used standards include:
1. International General Standards
(1) IEC 60068 (International Electrotechnical Commission Standards)
- IEC 60068-2-1 (Cold tests)
- IEC 60068-2-2 (Dry heat tests)
- IEC 60068-2-14 (Change of temperature tests)
- IEC 60068-2-30 (Damp heat, cyclic tests)
This series is widely used for electrical and electronic products, including components, PCBs, and batteries, to assess their reliability under different temperature and humidity conditions.
(2) MIL-STD-810 (U.S. Military Standard)
Primarily used in defense, aerospace, and automotive electronics. Relevant methods include:
- MIL-STD-810G Method 501.5 (High-temperature testing)
- MIL-STD-810G Method 502.5 (Low-temperature testing)
- MIL-STD-810G Method 503.5 (Temperature shock testing)
This standard is known for its rigorous requirements, suitable for testing equipment durability in extreme environments.
(3) ISO 16750 (Automotive Electronics Standard)
Specifically for automotive electrical and electronic equipment:
-
- ISO 16750-4 (Climatic loads)
- ISO 16750-3 (Mechanical loads)
It applies to in-vehicle electronics, sensors, batteries, etc., ensuring their stability under harsh conditions like severe cold or heat.

2. Industry-Specific Standards
(1) GB/T 2423 (Chinese National Standard)
- GB/T 2423.1 (Cold tests)
- GB/T 2423.2 (Dry heat tests)
- GB/T 2423.22 (Change of temperature tests)
Applicable to industries like electronics, telecommunications, and new energy within China, meeting domestic certification requirements.
(2) JIS C 0025 (Japanese Industrial Standard)
Mainly used for testing Japanese automotive and electronic equipment, e.g.:
- JIS C 0025-1999 (Temperature cycling test)
(3) AEC-Q100 (Automotive Electronics Council Standard)
Focuses on reliability testing for automotive-grade integrated circuits, including:
- AEC-Q100 Grade 0~3 (Tests for different temperature grades)
3. How to Choose the Right Test Standard?
Selecting the appropriate testing protocol depends on several factors:
- Industry Requirements: (e.g., military, automotive, consumer electronics)
- Product Application Environment: (e.g., arctic regions, tropical climates)
- Certification Needs: (e.g., CE, UL, CCC certification)
- Testing Purpose: (e.g., R&D validation, mass production quality control)
Examples:
- Consumer electronics (e.g., smartphones) typically use IEC 60068 or GB/T 2423.
- Automotive components (e.g., ECUs) need to comply with ISO 16750 or AEC-Q100.
- Military equipment must meet MIL-STD-810.

4. Application Examples of Thermal Shock Chambers
-
New Energy Vehicle Battery Testing
Power batteries must remain stable in environments ranging from -40°C to +85°C to prevent safety risks. Standards like IEC 62660 and GB/T 31467 are used to ensure battery performance under these extreme temperatures. -
Aerospace Equipment
Aircraft avionics must withstand rapid transitions between high-altitude cold (-55°C) and ground-level heat (+70°C). MIL-STD-810 testing verifies their reliability. -
5G Communication Equipment
Base station equipment must adapt to various global climates. The IEC 60068-2-14 temperature cycling test simulates long-term usage conditions.
In today's competitive market, product reliability is a key determinant of brand reputation. Thermal shock chambers are not just quality control tools but also a reflection of a company's technical capability. By adhering to international standards, companies can identify product flaws early, reduce post-market risks, and build customer trust.
Whether in electronics, automotive, defense, or new energy, selecting the appropriate test standards and optimizing testing processes are crucial for ensuring product stability and reliability under extreme conditions. Only products that pass rigorous testing can succeed in the global marketplace.