In the realms of industrial processing, materials science, and quality assurance, the precise control of thermal environments is paramount. Two cornerstone instruments in this domain are the Vacuum Drying Oven and the High-Temperature Test Chamber. While superficially similar in their application of heat, their design philosophies, operational principles, and intended applications are fundamentally distinct. Misapplication can lead to product failure, inaccurate data, and significant financial loss. This white paper provides a rigorous, detailed comparison of these two critical pieces of equipment. It elucidates their unique functionalities, core technological differentiators, and ideal use cases, empowering engineers, researchers, and procurement specialists to make informed, optimal decisions that ensure process integrity, enhance product reliability, and accelerate innovation.
1. Introduction: The Criticality of Precision Thermal Processing
The advancement of modern technology is inextricably linked to our ability to manipulate and test materials under controlled conditions. Thermal processing is a ubiquitous requirement, but the specifics of the application dictate the necessary technology. The conflation of a Vacuum Drying Oven with a High-Temperature Test Chamber is a common but costly error. One is a precision removal tool, the other a rigorous simulation and validation engine. Understanding this dichotomy is not merely academic; it is a operational necessity for any organization committed to excellence in R&D, manufacturing, and quality control.
This document serves as a definitive guide, dissecting the architecture, operation, and purpose of each system. We will demonstrate how [Your Company Name]’s engineering expertise delivers unparalleled performance and reliability in both categories, providing tailored solutions that meet the exacting standards of global industries.

2. In-Depth Analysis: The Vacuum Drying Oven
2.1. Core Function and Principle:
The primary function of a Vacuum Drying Oven is the gentle and efficient removal of moisture, solvents, and other volatiles from a sample without causing thermal degradation. Its operation is predicated on a simple principle of physics: reducing the pressure within the chamber lowers the boiling point of liquids.
By evacuating the chamber to pressures often as low as 1 x 10⁻³ mbar or beyond, water and solvents vaporize at temperatures far below their standard atmospheric boiling points. For instance, water can be made to boil at room temperature under a sufficient vacuum. This allows for the drying of heat-sensitive materials—such as pharmaceuticals, delicate chemicals, and electronic components—that would otherwise decompose, oxidize, or change form at higher temperatures.
2.2. Key Design Features:
- Vacuum System: The heart of the oven. It consists of a robust, airtight chamber (often constructed of 304 or 316 stainless steel for corrosion resistance) and a vacuum pump. The pump's performance (ultimate vacuum level and pumping speed) is a critical specification.
- Heating System: Heating is typically achieved through electric heating elements. However, in a vacuum, convection heating is impossible due to the lack of air. Therefore, heat transfer occurs primarily via radiation and conduction (through the shelves and sample trays). This leads to less thermal gradient than one might expect, as radiant heat permeates the chamber evenly.
- Control and Safety: Precise digital controllers regulate temperature. A vacuum gauge is essential for monitoring chamber pressure. Safety features include over-temperature protection and automatic vacuum release valves to prevent implosive pressures or oven deformation upon opening.
2.3. Primary Applications:
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Drying heat-sensitive APIs (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients), powders, and glassware without compromising molecular stability.
- Electronics Manufacturing: Curing and drying of epoxy resins, removing moisture from PCBs post-wash to prevent "popcorning" during soldering, and drying semiconductors.
- Chemical and Plastics Industries: Removing solvents from samples gently to prevent reaction or evaporation.
- Research Laboratories: Drying delicate biological samples, preparing samples for analysis (e.g., for SEM or spectroscopy), and degassing polymers and rubbers.

3. In-Depth Analysis: The High-Temperature Test Chamber
3.1. Core Function and Principle:
The primary function of a High-Temperature Test Chamber (often called an Environmental Test Chamber or Thermal Aging Oven) is to simulate harsh temperature conditions to assess a product's durability, reliability, and performance under stress. Its purpose is not removal but acceleration and evaluation.
These chambers subject test specimens to precisely controlled elevated temperatures—often exceeding 300°C, with some models reaching 500°C or more—for extended periods. The goal is to accelerate the aging process, identify failure modes, validate product design, and ensure compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM, MIL-STD).
3.2. Key Design Features:
- High-Temperature Capability: The defining feature. Heating systems are engineered for extreme heat, utilizing high-wattage heating elements and advanced insulation materials (e.g., mineral wool) to ensure chamber integrity and energy efficiency.
- Forced Air Convection: This is the critical differentiator. A powerful blower motor circulates air continuously throughout the chamber at high velocity. This ensures exceptional temperature uniformity (±1.0°C or better is standard for premium models) across the entire workspace, which is non-negotiable for valid test results. Every sample, regardless of location, experiences the same thermal conditions.
- Robust Construction: Built to run continuously for days or weeks. Construction is heavy-duty, with reinforced structures and doors sealed with high-temperature gaskets to prevent heat loss.
- Advanced Control and Programming: Sophisticated programmable controllers allow users to create complex temperature profiles (ramping, soaking, cycling) and store recipes for repeatable testing. Data logging capabilities are essential for audit trails and reporting.

3.3. Primary Applications:
- Automotive and Aerospace: Testing components like engine parts, composites, seals, and electronics for longevity under hood or avionics bay temperatures.
- Electronics Reliability (HALT & HASS): Highly Accelerated Life Testing and Stress Screening to rapidly uncover design weaknesses and production defects in electronic assemblies.
- Material Science: Studying the thermal aging of polymers, plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites to determine lifespan and degradation points.
- Quality Assurance & Compliance: Verifying that products meet specific industry standards for thermal endurance before they reach the market.
4. Head-to-Head Comparison: A Technical Dissection
| Feature | Vacuum Drying Oven | High-Temperature Test Chamber |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Objective | Gentle removal of volatiles (moisture, solvents) | Simulation of high-temp environments for testing and aging |
| Operating Atmosphere | Low-pressure vacuum (sub-atmospheric) | Ambient air or controlled atmosphere (sometimes with fresh air purge) |
| Heat Transfer Mechanism | Radiation and Conduction | Forced Convection (primary) and Radiation |
| Key Performance Metric | Ultimate Vacuum Level (mbar/Torr) | Temperature Uniformity (±°C) across the workspace |
| Typical Max Temperature | Moderate (150°C - 250°C is common) | Very High (200°C - 500°C+) |
| Critical Component | Vacuum Pump & Sealed Chamber | High-velocity Blower Motor & Heating Elements |
| Sample Impact | Prevents oxidation, boiling, and degradation | Induces thermal stress to force and observe failures |
5. Why the Distinction Matters: The Cost of Misapplication
Choosing the wrong equipment can have dire consequences:
- Using a Vacuum Oven for a Test Application: Placing a product for thermal aging test in a vacuum oven would yield invalid results. The lack of forced convection creates significant temperature gradients; samples on different shelves would age at different rates. The test would be unrepeatable and non-compliant with any standard, leading to false confidence in a product's reliability.
- Using a Test Chamber for a Drying Application: Subjecting a solvent-laden sample to high temperatures with forced air convection is extremely hazardous. It can cause rapid, uncontrolled evaporation, leading to explosive atmospheres within the chamber, potential ignition, and severe safety risks. Furthermore, it would likely destroy the sample through thermal shock or oxidation.
6. [Your Company Name]: Engineering Excellence for Every Application
At [Your Company Name], we do not merely sell ovens; we provide engineered thermal solutions. Our decades of expertise are embedded in every product we design, ensuring that whether your need is for gentle desiccation or rigorous testing, you receive a instrument of unmatched quality, precision, and durability.
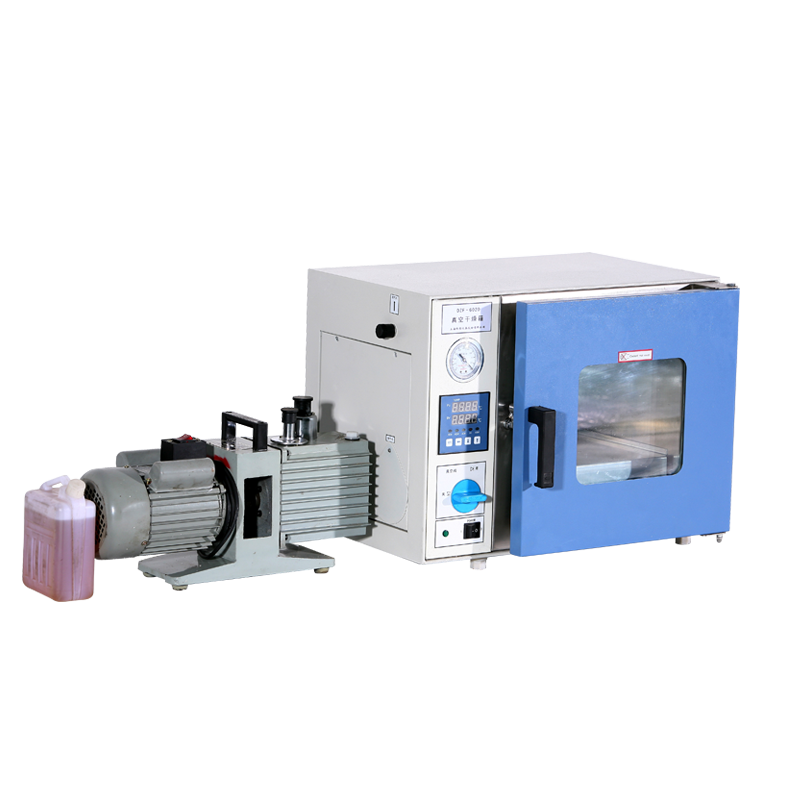

Our Vacuum Drying Ovens Feature:
- Superior Chamber Integrity: CNC-welded 304/316 stainless steel chambers with high-grade door seals guarantee a leak-free vacuum, ensuring rapid pump-down and holding ultimate vacuum levels consistently.
- Precise & Safe Control: Intuitive PID controllers with multi-stage programming, real-time vacuum and temperature display, and comprehensive safety lockouts protect both your samples and your investment.
- Configurable Options: A range of vacuum pump sizes, shelf configurations, and internal dimensions to perfectly match your process requirements.
Our High-Temperature Test Chambers Feature:
- Unrivaled Temperature Uniformity: Our proprietary airflow design and high-mass heating systems achieve uniformity as tight as ±0.5°C, setting the industry benchmark for test validity.
- Robustness for Demanding Duty Cycles: Built to MIL-STD specifications, our chambers are engineered for 24/7 operation, with redundant safety systems and over-temperature protection to safeguard long-term, unattended tests.
- Advanced Programming & Data Management: Our touch-screen controllers offer limitless program steps, real-time graph display, and USB/Ethernet connectivity for seamless data export and remote monitoring, ensuring full compliance and traceability.
7. Conclusion: Making the Informed Choice
The choice between a Vacuum Drying Oven and a High-Temperature Test Chamber is a strategic decision dictated by a fundamental question: Is the goal gentle removal or rigorous testing?
The Vacuum Drying Oven is the undisputed solution for processes where the preservation of sample integrity is paramount, leveraging the power of vacuum to enable low-temperature evaporation. Conversely, the High-Temperature Test Chamber is an essential tool for validation and quality engineering, using precisely controlled, uniform high heat to push products to their limits and beyond.
By understanding these critical differences, organizations can optimize their processes, ensure the safety of their operations, and generate data that is both reliable and defensible. [Your Company Name] stands ready to be your partner in this endeavor. Our technical experts are available to consult on your specific application, ensuring you select the perfect instrument to drive your innovation, quality, and success forward.