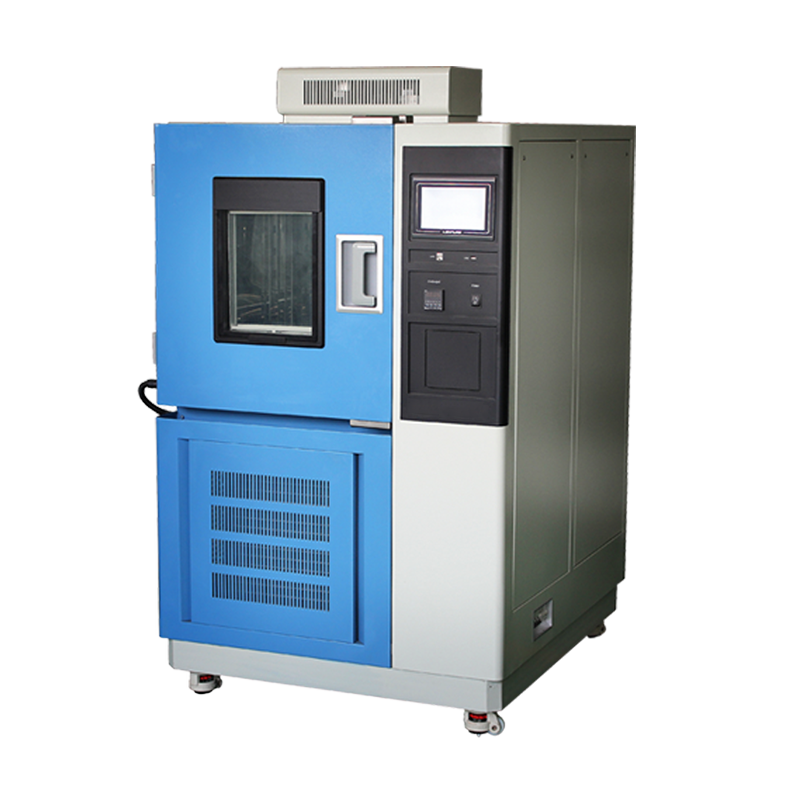
temperature chambers are the workhorses of labs, R&D centers, and production lines—but choosing the right one can feel like comparing apples to oranges. Three specs always dominate the conversation: temperature range, uniformity, and stability (often called “fluctuation”). Let’s break them down and figure out which one deserves top billing.
-
Temperature Range – the Gatekeeper
This is the headline spec: the lowest and highest temperatures the chamber can hit.
• Semiconductor stress testing may plunge to –70 °C.
• Pharmaceutical stability studies might sit at +85 °C.
If the range doesn’t cover your test window, nothing else matters.

-
Temperature Uniformity – the Accuracy Driver
Uniformity measures how evenly temperature is distributed throughout the workspace.
• Poor uniformity means one corner is 2 °C cooler than another, skewing material-strength data or battery-cycle-life results.
• Tight uniformity (±0.5 °C or better) is non-negotiable for multi-sample tests, calibration work, or any study where every degree counts. -
Temperature Stability – the Repeatability Metric
Stability tracks how much the setpoint drifts once the target temperature is reached—typically expressed as ±X °C over time.
• High stability (±0.1 °C) keeps long-term aging tests consistent.
• A chamber that “hunts” ±2 °C will introduce noise into thermal-cycling experiments and erode confidence in failure-analysis conclusions.
So which one wins?
There’s no universal victor—only the parameter that governs your specific application.
There’s no universal victor—only the parameter that governs your specific application.
• Range rules when you need extreme cold or heat; the other specs are irrelevant if you can’t even reach the target.
• Uniformity dominates when multiple samples share the same space or when small temperature differences can trigger large performance gaps.
• Stability reigns supreme for long-duration tests, cyclic profiles, or any protocol where repeatability is mission-critical.
• Uniformity dominates when multiple samples share the same space or when small temperature differences can trigger large performance gaps.
• Stability reigns supreme for long-duration tests, cyclic profiles, or any protocol where repeatability is mission-critical.
Bottom line: List your test requirements in order of risk, then rank the specs accordingly. A chamber that nails all three is ideal, but when trade-offs are necessary, let the application—not the brochure—decide.