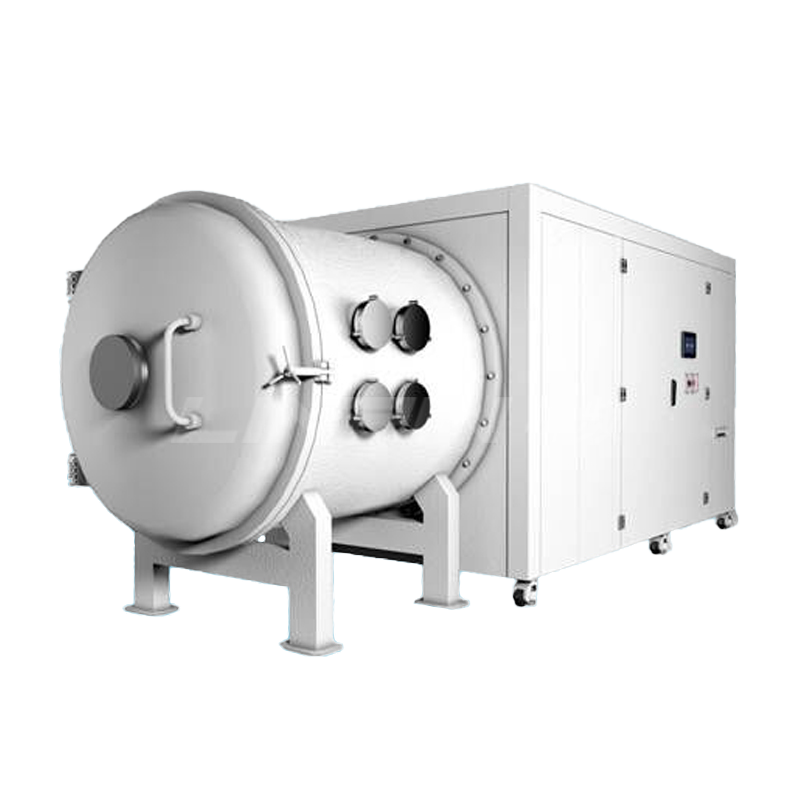
A thermal vacuum chamber is a device designed to simulate high-temperature and low-pressure environments, commonly used for researching and testing the performance of materials, products, or components. These chambers have broad applications across various industries, including materials science, electronics, aerospace, automotive, and energy. Below are some insights on how thermal vacuum chambers can enhance the efficiency of the R&D process:
-
Material Performance Testing – Thermal vacuum chambers can evaluate how materials behave under high-temperature and low-pressure conditions. This is crucial for developing new materials for extreme environments, such as those used in rocket engines or high-temperature equipment.
-
Product Reliability Testing – Manufacturers can use thermal vacuum chambers to simulate extreme operating conditions and assess product reliability and durability. This helps identify potential issues early, reducing the risk of failures in the market.

-
Accelerated Aging Testing – These chambers can replicate long-term aging processes, allowing researchers to quickly understand a product’s lifespan in real-world conditions. This is essential for developing durable products and minimizing maintenance costs.
-
Performance Optimization – By continuously testing and refining products or materials in thermal vacuum chambers, R&D teams can rapidly improve performance and shorten development cycles.
-
Reliability Validation – Conducting thermal vacuum tests at various stages of development ensures that products can function reliably under extreme conditions, reducing the need for costly post-launch fixes and maintenance.
-
Regulatory Compliance – In certain industries, thermal vacuum testing is mandatory to ensure products meet specific standards and regulations.
Thermal vacuum chambers enable R&D teams to develop high-performance, durable, and reliable products more efficiently. By simulating extreme conditions, potential issues can be identified and resolved before market deployment, saving both time and resources. However, proper operation is essential to ensure testing accuracy and repeatability.