Aging test chambers typically consist of a circulation system, heating system, and over-temperature exhaust system, all installed at the top of the aging chamber to avoid occupying additional space.
-
Circulation System:
A circulation fan and matching air ducts ensure uniform temperature distribution within the test area. The circulation system remains continuously operational during the aging process to maintain temperature consistency. The entire system features stable performance, precise control, minimal temperature fluctuations, high uniformity, and low noise levels. -
Heating System:
Electric heaters are used for heating and are installed in the circulation duct on the chamber’s ceiling, surrounded by fireproof insulation. The heaters include overheat protection. If the tested product generates heat, an overheat exhaust system is activated:- For low heat output, motorized louvers provide automatic negative-pressure exhaust.
- For high heat output, low-noise exhaust fans with variable frequency drive (VFD) control are used.
Once the target temperature is reached, the heater adjusts its power based on real-time temperature fluctuations, working in tandem with insulated panels to maintain precise and stable temperature control. Heating stops when the set temperature is achieved.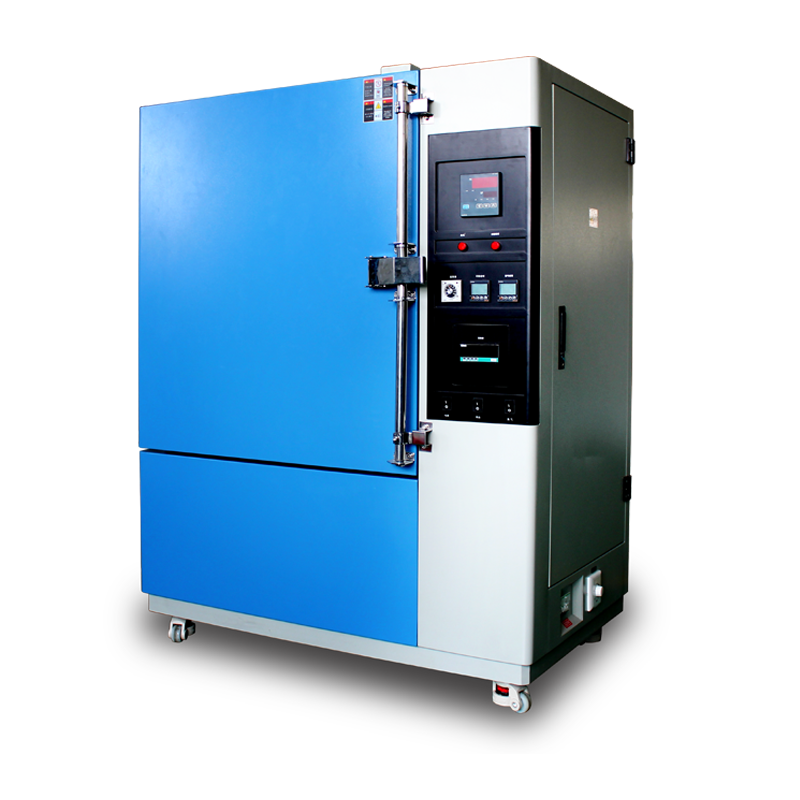 
-
Over-Temperature Exhaust System:
Upon startup, the heater begins warming the chamber. When the set temperature is reached, heating stops. Over time, the product area may gradually overheat. If the temperature exceeds the upper limit, the exhaust system activates to expel hot air outside. A VFD controls the exhaust fan speed, stopping the fan and closing the exhaust system once the temperature drops to the lower limit. -
Noise Treatment:
- Low-decibel, high-quality circulation fans are used.
- Air ducts are wrapped with 3 cm thick asbestos for both insulation and noise reduction.
- Flexible connections (e.g., canvas and springs) are applied to all moving parts to minimize noise to the lowest standard.