As global climate change becomes increasingly severe, the development and utilization of renewable energy have become a key focus of energy policies worldwide. Solar and wind energy are two major forms of renewable energy, offering advantages such as environmental friendliness, renewability, and pollution-free operation. They are widely used in electricity generation, hot water supply, and other fields. However, solar and wind power systems are highly susceptible to climatic conditions. Long-term exposure to outdoor environments makes them vulnerable to weather-related factors, which can impact their performance and lifespan.
To assess the long-term stability of solar panels and wind turbines when exposed to outdoor conditions, researchers have developed ozone aging test chambers. These chambers simulate climatic conditions such as solar radiation, high temperatures, and humidity, enabling accelerated aging tests to evaluate the performance and durability of solar panels and wind turbines under harsh weather conditions.
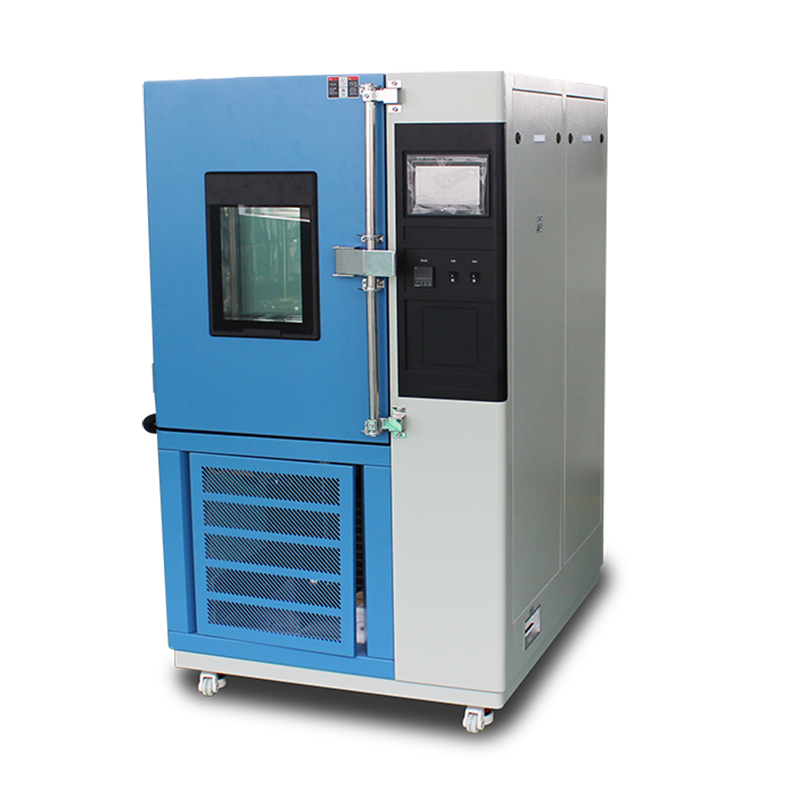

In an ozone aging test chamber, researchers place solar panels and wind turbines inside the testing compartment and control parameters such as temperature, humidity, and ozone concentration to replicate natural outdoor climatic conditions. Over a specified period, researchers can observe changes in the performance of the solar panels and wind turbines, gaining insights into their stability under different weather scenarios.
Through testing in ozone aging chambers, researchers can evaluate the long-term stability of solar panels and wind turbines under adverse climatic conditions, providing valuable references for their real-world performance and lifespan. This testing method helps researchers optimize the design and material selection of solar and wind power systems, enhancing their reliability and durability in harsh environments and promoting the advancement and adoption of renewable energy.