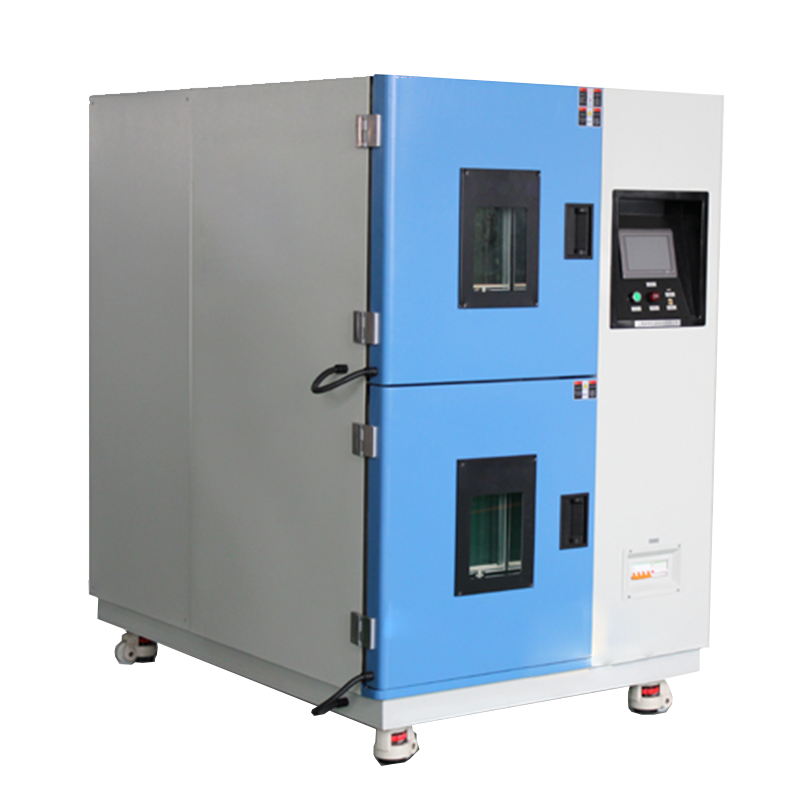
A thermal shock test chamber is a device used to evaluate the performance of materials and products under extreme temperature variations. It simulates rapid temperature changes to assess the durability and stability of materials under alternating hot and cold conditions. This equipment is commonly employed in the research, development, and quality control of electronic components, aerospace, automotive, plastics, and other industrial products.
The advantages of using a dual-cascade refrigeration system in thermal shock test chambers are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
-
Faster Temperature Transition Rates: The dual-cascade refrigeration system enables quicker temperature changes, meeting testing requirements with higher demands for transition speeds.
-
Higher Refrigeration Efficiency: The cascade design optimizes refrigeration efficiency across different temperature ranges, improving overall energy efficiency and reducing power consumption.

-
Broader Temperature Range: The dual-cascade refrigeration system provides a wider temperature testing range, making it suitable for thermal shock tests on various materials and products.
-
Enhanced Stability: The two-unit system can complement each other during operation, improving system stability and reliability while minimizing the risk of malfunctions.
-
Extended Equipment Lifespan: Since the dual-cascade refrigeration system shares the cooling load, it reduces the operational strain on a single unit, thereby prolonging the equipment’s service life.
-
Flexibility and Scalability: The dual-unit system allows for flexible configurations based on actual needs, facilitating future expansions and upgrades.
-
Redundancy Design: If one refrigeration unit fails, the other can continue operating, ensuring test continuity and reliability.
Thermal shock test chambers equipped with dual-cascade refrigeration systems offer significant advantages in performance, efficiency, and reliability, better fulfilling diverse testing requirements.